Unit: AM/FM Stereo Receiver
Manufacturer: Pioneer
Model: SX-727
SN: TE3729669
One of my customers brought in this beautiful vintage receiver for restoration. It has been taken with care and is still in a perfect cosmetic condition but has some issues typical for 40-50 years old electronic equipment. Most original incandescent bulbs burned out, the stereo indicator bulb was replaced before but burned out again, all pots and switches are dirty and/or oxidized due to age. The SELECTOR switch was mostly affected in this receiver and didn't work properly when a PHONO source was selected. As a result, it was impossible to get a clear sound from a turntable. I restored this beautiful receiver and serviced all boards except a tuner section. Well, the tuner board was also serviced but I just replaced the electrolytic capacitors installed in a signal path on this board. It is usually safe to do and will not require any tuner re-alignment.
The Pioneer SX-727 was introduced in 1972 and delivers 37 watts per channel into 8 ohms with total harmonic distortion under 0.5%. It is a great mid-range receiver with a very sensitive and selective FM section offering distortion-free reception. A low noise field effect transistor in the first stage and a two-step RF amplifier provide an excellent sensitivity of 1.8 micro-volts (!) and a high signal-to-noise ratio of 70dB. I was able to get a stable stereo reception even without any external FM antenna attached! The SX-727 has terminals to connect two turntables, two tape decks, three pairs of speaker systems, and a microphone. The walnut-finish wooden cabinet looks beautiful and the build quality is excellent. A test report on the Pioneer SX-727 completed by the Hirsch-Houck Lab was published in Stereo Review magazine (July 1972, p. 34). The list price in 1972 was $349.95 (Ref. Stereo Review, March 1972, page 1). According to the Pioneer database, this unit was manufactured in May 1973.
Power Supply Board
The power supply circuit (#AWR-011) in Pioneer SX-727 has a similar design as a power supply circuit (#AWR-010) in Pioneer SX-828. And as might be expected both boards have similar problems. Two transistors Q1 and Q3, and the resistor R9 are running very hot on this board under normal operating conditions. The heat sink attached to transistors Q1 and Q3 is secured by a nylon screw. Due to high temperature and aging, this screw becomes brittle over time and easily breaks down. The metal oxide resistor R9 has a rated power of 2W which is usually not enough to efficiently dissipate the electrical power as heat. As a result, the part of PCB around this resistor is often found damaged. I replaced resistor R9 with a flameproof 3W metal oxide resistor to improve its heat dissipation. Also, it always makes sense to replace transistors Q1 and Q3 with Fairchild MJE transistors due to better thermal characteristics in comparison to original transistors. Five electrolytic capacitors C6, C7, C9, C10, and C11 were replaced with low impedance and high-reliability Nichicon UPW/UPM caps. The maximum operating temperature of new electrolytic capacitors is +105C which is also beneficial in power supply circuits. The original e-caps installed in vintage gears from the 70's have a maximum operating temperature of +85C.
Power supply board (#AWR-011) - PCB discoloration due to excessive heat from resistor R9
Original Sanyo power transistor and modern Fairchild MJE substitution
Power supply board (#AWR-011) - before and after
Protection Board
There are two versions of the protection board in Pioneer SX-727: #AWM-011 (early version) and #AWM-027 (later version). This receiver has the later version of the protection board. Also, the later version (#AWM-027) has several modifications and this particular one has two capacitors C1 and C2 as 0.22uF/10V electrolytic caps instead of Mylar caps. These two caps are the notorious sky blue Sanyo e-caps. These e-caps have a bad reputation to become very leaky over time. For more information about sky blue Sanyo e-caps refer to my previous post on Pioneer SX-828 restoration. I replaced C1 and C2 with high-quality film polyester Kemet caps. The remaining e-caps C3 thru C6 were replaced with low impedance and high-reliability Nichicon UPW caps.
Protection board (#AWM-027) - before and after
Head Amplifier Board
The head amplifier board in Pioneer SX-727 has six NPN transistors Q1 thru Q6. According to the service manual, these transistors could be either 2SC871 or 2SC458. However, in some units, the 2SC1312 transistor can be also found in these positions. All of these transistors are known to become very noisy over time. I replaced six original 2SC1312 transistors installed in this receiver with modern low noise Fairchild KSC1845. All new transistors were carefully matched by current gain and base-emitter voltage within 1%. Watch the pinout on replacement transistors while servicing this board. The original transistor is BCE and the new one is ECB.
Electrolytic capacitors C1/C2 and C5/C6 installed in the signal path were replaced with low leakage Nichicon UKL caps. The remaining e-caps C3/C4 and C15 were replaced with low impedance and high-reliability Nichicon UPW caps.
Head amplifier board (#W21-002) - before and after
AF Amplifier Board
The most difficult circuit board to work on in Pioneer SX-727 is an AF amplifier board (#AWK-010). This is a double solder PCB and requires a lot of patience while unsoldering and soldering the electronic components. There is always a risk of overheating and damaging this board while unsoldering electronic components. So, take your time and be very careful while servicing the AF amplifier board.
All original coupling capacitors C13/C14, C21/C22, and C27/C28 installed on this board are the notorious sky blue Sanyo electrolytic caps. I replaced e-caps C13/C14 and C21/C22 with low leakage Nichicon UKL caps. The e-caps C27/C28 are rated at 1uF/25V and I replaced them with high-quality film polyester WIMA MKS2 caps. In general, I replace all electrolytic capacitors with capacitance from 0.1uF to 1uF with film polyester caps. The remaining eight e-caps on this board were replaced with low impedance and high-reliability Nichicon UPW caps.
Two NPN transistors Q5 and Q6 installed on this board are 2SC1312. I replaced them with modern low noise Fairchild KSC1845. Watch the pinout on replacement transistors. The original transistor is BCE and the new one is ECB. I also replaced two PNP transistors Q3 and Q4 with modern low noise Fairchild KSA992. The original PNP transistors are 2SA725 and become very noisy over time.
The access to the pots and switches installed on the AF amplifier board is very limited when it is assembled to the chassis. But everything can be easily cleaned when it is disassembled from the chassis. I used the DeoxIT 5% as a contact cleaner and DeoxIT FaderLube 5% spray for subsequent lubrication.
AF amplifier board (#AWK-010) - before servicing
Power Amplifier Board
The power amplifier board (#AWH-011) has six electrolytic capacitors C7 thru C10, C15, and C16. I replaced two e-caps C7 and C8 with low leakage Nichicon UKL caps. The remaining four e-caps were replaced with low impedance and high-reliability Nichicon UPW/UPM caps. As can be seen from the test results four out of six e-caps on this board are out of factory spec.
Test results on original capacitors removed from Power Amplifier board:
C7: rated capacitance – 22uF, measured capacitance – 31uF, deviation: +41% (out of spec)
C8: rated capacitance – 22uF, measured capacitance – 30uF, deviation: +36% (out of spec)
C9: rated capacitance – 220uF, measured capacitance – 307uF, deviation: +40% (out of spec)
C10: rated capacitance – 220uF, measured capacitance – 323uF, deviation: +47% (out of spec)
C15: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured capacitance – 106uF, deviation: +6% (Okay)
C16: rated capacitance – 100uF, measured capacitance – 106uF, deviation: +6% (Okay)
Two NPN transistors Q5 and Q6 installed on the power amplifier board are Sony 2SC1124. The current gain in the 2SC1124 transistor degrades with age. The modern substitution is a Fairchild KSC2690A transistor. I replaced the original Sony transistors with KSC2690A to prevent any issues in the future. Watch the pinout on replacement transistors. The original transistor is EBC and the new one is ECB.
Power amplifier board (#AWH-011) - before and after
Dial and Meter Lamps
Two fuse-type lamps installed behind the tuning and signal strength meters are relatively easy to change in Pioneer SX-727. Just unscrew two small screws on the top and the lamp holder will be easily released from the chassis. The original incandescent bulbs installed in the lamp holder usually overheat the plastic on the meters and discolors it. As a result, the plastic often becomes yellowish. One possible solution to overcome this issue is to install cool blue LED lamps. These LED lamps are brighter than original incandescent bulbs but generate almost no heat and virtually last forever.
Original incandescent bulbs installed behind the tuning and signal strength meters
New cool blue LED lamps installed
Yellowish plastic due to extensive heat from original incandescent bulbs
To replace 5 dial lamps I pulled off all knobs from shafts, removed nuts and washers from their shafts, removed a faceplate, and then carefully removed four clips holding a dial scale. This process is similar to that I described in detail during the Pioneer SX-828 restoration.
New cool blue LED lamps installed
The original stereo indicator bulb in this unit was replaced by somebody in the past but burned out again. It looks like the technician or whoever he was doesn't possess good soldering skills as can be seen in the photo below. I installed a warm white LED lamp here and secured it with super glue. The new LED lamp will virtually last forever.
Stereo indicator bulb replaced by somebody in the past - sloppy work!
Stereo indicator bulb replaced with warm white LED lamp
Bias and DC Offset Adjustments
At the end of my restoration, I checked and adjusted the Bias and DC offset on the power amplifier unit. The service manual has no description for these adjustments but this procedure is pretty much straightforward.
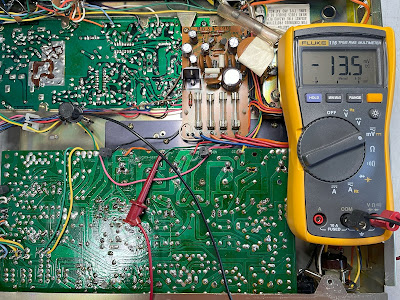
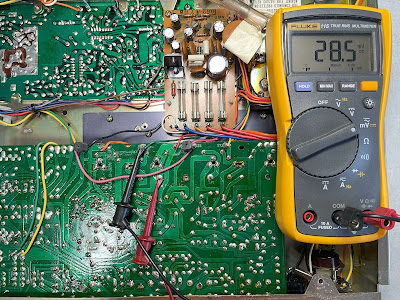
The bias is measured between pins 11 and 13 on the left channel, and between pins 12 and 14 on the right channel. It should be adjusted to ~20mV with trimmer VR3 and VR4, respectively.
The DC offset is measured between pin 5 and ground on the left channel, and between pin 6 and ground on the right channel. It should be adjusted as close to zero volts as possible with trimmer VR1 and VR2, respectively.
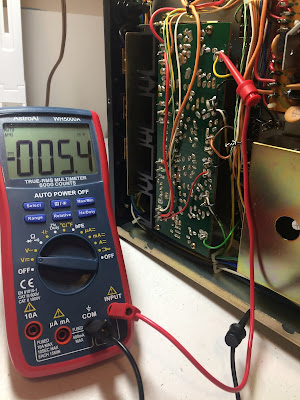
Bias on the left and right channel after restoration
DC offset on the left and right channel after restoration
The final result can be seen in the photos below. The receiver looks beautiful and has enough power to fill a large room with great sound. Please watch a short demo video at the end of this post. Thank you for reading.
Pioneer SX-727 - before restoration


































_disassembled%20from%20the%20chassis.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)
_before%20servicing.jpg)
_after%20servicing.jpg)